
Analysis of 6.7L Powerstroke Delete Pipe: Guide for Weighing the Pros and Cons
The Ford 6.7-liter Powerstroke diesel engine, with its powerful 475 horsepower, has set a performance benchmark in the heavy-duty towing sector. However, modern environmental standards have placed a sophisticated "environmental restraint" on this beast. While this complex system purifies the exhaust gases, it also subtly alters the engine's operation mode.
This article will delve deeply into the core of the 6.7-liter Powerstroke's emission control, particularly the crucial diesel particulate filter system. We will strip away the layers of technical jargon to examine how it operates in daily use, explore the potential chain reactions it may trigger, and objectively analyze the realistic choices and trade-offs that owners face when this system itself becomes a "problem".
Understanding the 6.7L Powerstroke Emissions System
To meet stringent EPA Tier 4 emissions standards, Ford implemented a multi-stage aftertreatment system on the 6.7L Powerstroke:
- Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF): Captures and stores soot particles.
- Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC): Converts carbon monoxide (CO) and unburned hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O).
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR): Uses Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) to break down nitrogen oxides (NOx) into harmless nitrogen and water.
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR): Recirculates a portion of exhaust gas back into the combustion chambers to lower peak temperatures and reduce NOx formation.
How the DPF Works & The Regeneration Process
The DPF is a honeycomb-style ceramic filter located downstream of the turbocharger. Its microscopic pores trap soot particles as exhaust gases flow through. Over time, this trapped soot increases exhaust backpressure.
To prevent excessive clogging, the engine's computer initiates a regeneration cycle:
-
Passive Regeneration: Occurs naturally during sustained highway driving when exhaust temperatures are sufficiently high to burn off soot continuously.
-
Active Regeneration: The engine's computer detects a full filter during normal driving. It then injects extra fuel into the exhaust stroke to dramatically increase exhaust temperature, oxidizing the trapped soot.
Common Problems Associated with the DPF System
-
Frequent or Failed Regenerations: Short-trip, stop-and-go driving prevents the DPF from reaching necessary temperatures, leading to incomplete cycles and warning lights.
-
Increased Backpressure & Reduced Performance: A clogging DPF restricts exhaust flow, leading to noticeable losses in power, throttle response, and fuel economy.
-
Fuel Dilution of Engine Oil: During active regenerations, unburned fuel can slip past piston rings and contaminate the engine oil, degrading its lubricating properties and potentially causing premature wear.
-
High Maintenance/Replacement Costs: The DPF has a finite service life. Eventually, it becomes saturated with non-combustible ash and requires very expensive professional cleaning or full replacement.
Should the DPF System be Removed?
Alternatives to a Full Delete Kit
Before considering removal, explore these options:
Professional DPF Cleaning:
A specialized service can remove, clean, and restore a moderately clogged filter for a fraction of the cost of a new one. This is a viable solution if the filter's substrate is still intact.
Driving Habit Modification:
Ensuring the truck completes regeneration cycles by taking it on weekly extended highway drives can significantly prolong DPF life.
Forced Stationary Regeneration:
Using a high-level diagnostic scanner, a technician can manually initiate a full regeneration cycle while the vehicle is parked.
When Might a Delete Pipe Be Considered?
The decision to remove the DPF and related components (EGR, SCR) is significant and often driven by specific circumstances:
High-Mileage Vehicles with Repeated Failures:
When facing a second or third major DPF/SCR system repair on a truck with over 120,000 miles, the cost of a delete kit may be lower than continued OEM repairs.
Dedicated Heavy Towing or Commercial Use:
For trucks constantly under severe load, removing the system can reduce exhaust gas temperatures (EGTs), eliminate regeneration interruptions during critical tasks, and improve load-hauling fuel efficiency.
Off-Road/Competition Vehicles:
For trucks used exclusively off-public roads or in competition, removing emissions equipment can maximize performance and reliability without regulatory concerns.
Pursuit of Maximum Long-Term Reliability:
Some owners prioritize simplifying the engine system by removing components known to be potential failure points, accepting the legal and environmental trade-offs.
Featured Performance Solutions: DPF & EGR Delete Kits
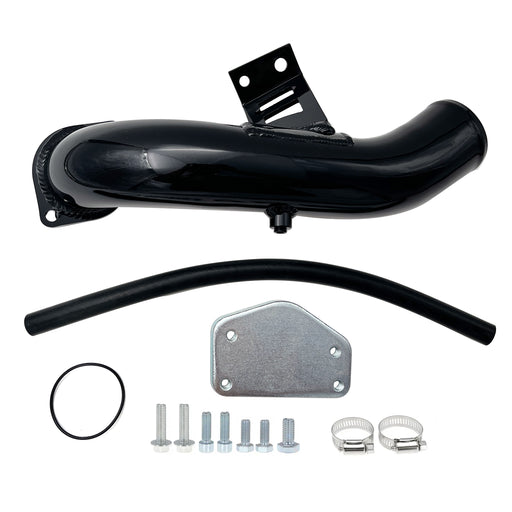
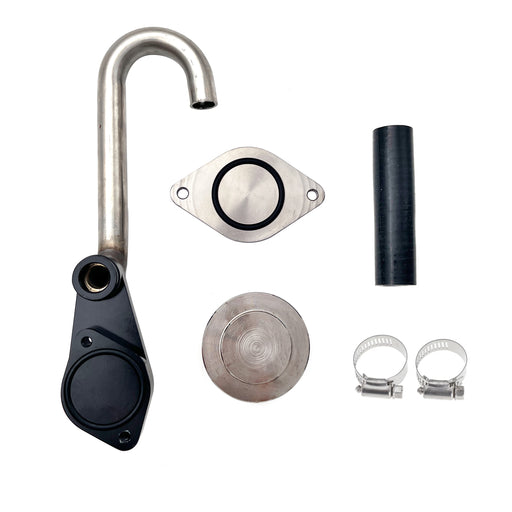
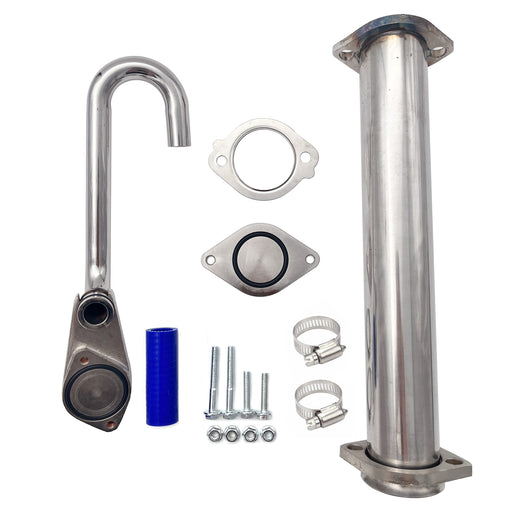
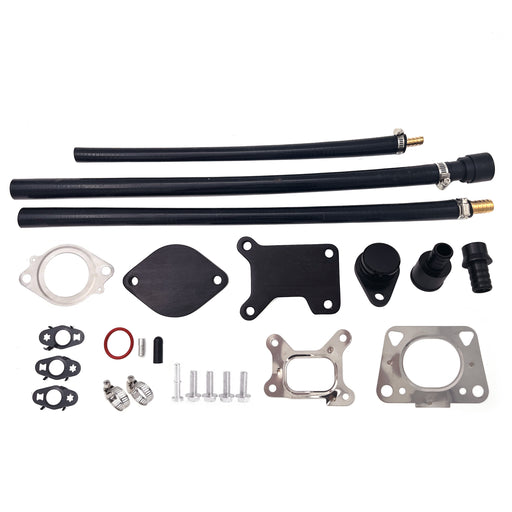
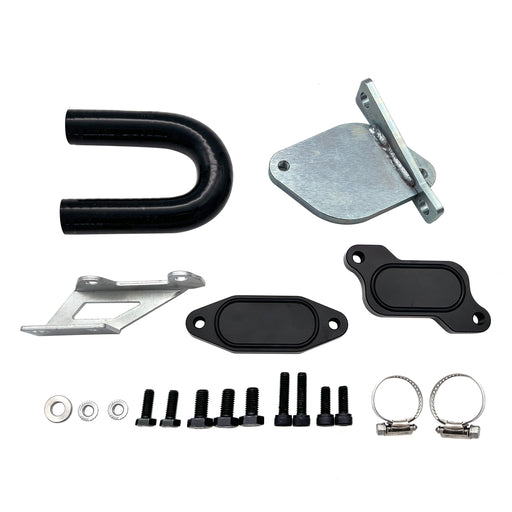
2011-2023 6.7L Ford Powerstroke 4" Exhaust Delete Pipe & EGR Delete Kit
This comprehensive kit synergistically combines DPF and EGR deletion into one integrated system for superior drivability and durability.

-
Enhanced Breathing & Combustion: Eliminates exhaust backpressure at the turbo outlet while preventing recirculation of soot-laden exhaust gases. This allows the engine to intake only clean, oxygen-rich air for more efficient combustion.
-
Improved Thermal Management: The integrated EGR delete kit accelerates cooling system circulation, helping to maintain lower overall engine temperatures during heavy loads.
-
Eliminated Maintenance Points: Permanently removes the need for DPF regenerations, filter replacements, EGR valve cleanings, and cooler repairs—drastically reducing long-term operating costs and failure risks.
- Optimized for Real-World Use: Provides the ideal balance of increased throttle response, reliable power gains, and enhanced durability for demanding street driving, towing, and daily use.
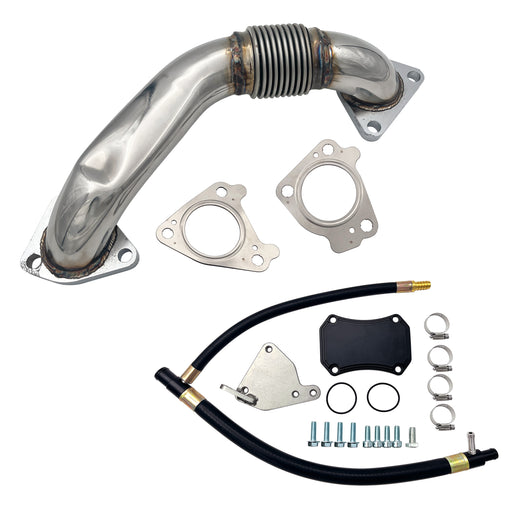
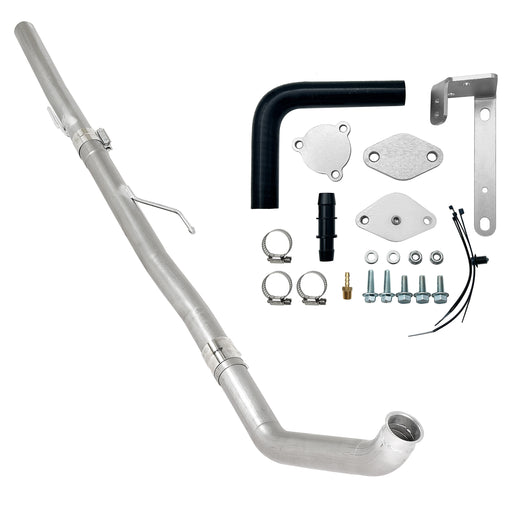
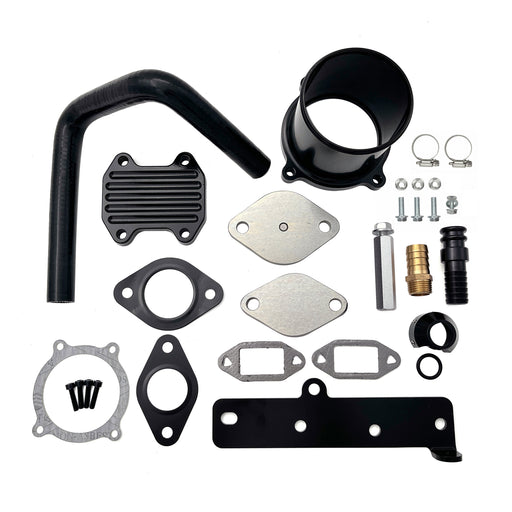
4"/5" Dp-Back DPF Delete Pipe & EGR Delete for 2011-2022 6.7L Ford Powerstroke
Engineered for ultimate performance, this DPF & EGR delete kit prioritizes unrestricted flow and heat reduction through its integrated design.

-
Maximized Exhaust Flow: Features a 5.0-inch straight-through T-409 stainless steel exhaust path that virtually eliminates all turbo backpressure, complemented by a complete EGR system removal to prevent exhaust gas recirculation.
-
Competition-Ready Configuration: Straight-pipe design (with optional muffler) ensures zero restriction for peak horsepower and torque in racing or off-road environments.
-
Superior Thermal Efficiency: The dual-action approach—removing both exhaust restrictions and hot EGR gases—significantly lowers exhaust gas temperatures (EGTs) and reduces overall engine bay heat.
- Enhanced Turbo Response: By eliminating backpressure and preventing exhaust gas recirculation, the turbocharger spools faster with less thermal loading, delivering immediate throttle response.
- Professional Integration: Includes black anodized components for durability and a pre-tapped 12mm port for seamless factory EGT probe installation.
Featured collection
-
Seguler 1986-1995 Ford F150 F250 F350 Mustang Trucks EGR Simulator Eliminator / Block Off Plate Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $79.99 - Original price $79.99Original price$79.99$79.99 - $79.99Current price $79.99Block Off Plate Material: Aluminum alloy. Easy installation,and convenient to use. Made of CNC milled from aircraft grade Billet aluminum. Will N...
View full detailsOriginal price $79.99 - Original price $79.99Original price$79.99$79.99 - $79.99Current price $79.99 -
Seguler 2009-2019 6.7L Ram Cummins Coolant Bypass Barb Adapter Leak Repair Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $35.99 - Original price $35.99Original price$35.99$35.99 - $35.99Current price $35.99Made of aerospace-grade billet aluminum. Effectively repair the problem of coolant leakage. Resist corrosion and rust for a long time and has good...
View full detailsOriginal price $35.99 - Original price $35.99Original price$35.99$35.99 - $35.99Current price $35.99 -
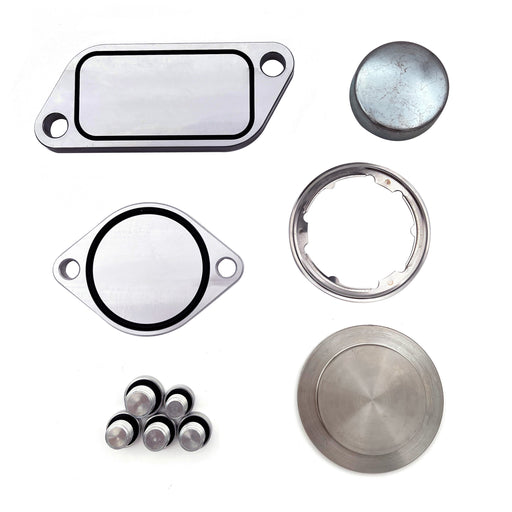
For 2011-2023 6.7L Ford Powerstroke Diesel EGR Delete Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $109.99 - Original price $109.99Original price$109.99$109.99 - $109.99Current price $109.99Material: Aluminum alloy,Stainless steel. 10mm Hole exhaust cover plate for Ford EGT Probes. CNC machine of billet aluminum and stainless steel m...
View full detailsOriginal price $109.99 - Original price $109.99Original price$109.99$109.99 - $109.99Current price $109.99 -
For 1996-2004 3.8L 4.6L 5.4L Ford GT SVT GT500 V8 Mustang Cobra EGR Delete kit And Exhaust Cap
SEGULEROriginal price $51.99 - Original price $51.99Original price$51.99$51.99 - $51.99Current price $51.99Placement on Vehicle:Front Billet aluminum IAC (idle air control) and EGR (exhaust gas recirculation) block-off plates add a distinctive touch to ...
View full detailsOriginal price $51.99 - Original price $51.99Original price$51.99$51.99 - $51.99Current price $51.99 -
For 2011-2016 6.6L GMC Chevy Duramax Diesel LML EGR Valve Cooler Delete Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $66.49 - Original price $66.49Original price$66.49$66.49 - $66.49Current price $66.49Material: Stainless steel, billet aluminum. Eliminate soot and block of EGR valve prevent high EGT from flow back into engine. Quicker turbo spoo...
View full detailsOriginal price $66.49 - Original price $66.49Original price$66.49$66.49 - $66.49Current price $66.49 -
For 2010-Present Stage 2 ISX 15 CM2250 CM2350 EGR Delete Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $59.99 - Original price $59.99Original price$59.99$59.99 - $59.99Current price $59.99Material: Aluminum Two plates in this kit are made of 6061 aircraft grade billet aluminum anodized and CNC laser cut or CNC machined out of high q...
View full detailsOriginal price $59.99 - Original price $59.99Original price$59.99$59.99 - $59.99Current price $59.99 -
For 2011-2023 6.7L Ford Powerstroke Diesel EGR Delete Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $85.99 - Original price $85.99Original price$85.99$85.99 - $85.99Current price $85.99Material: Aluminum alloy,Stainless steel. 10mm Hole exhaust cover plate for Ford EGT Probes. CNC machine of billet aluminum and stainless steel m...
View full detailsOriginal price $85.99 - Original price $85.99Original price$85.99$85.99 - $85.99Current price $85.99 -
For 2004-2005 6.6L Chevy GMC Silverado LLY Duramax Diesel EGR Delete Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $92.99 - Original price $92.99Original price$92.99$92.99 - $92.99Current price $92.99Material: Aluminum,Stainless steel,Silicone Eliminates soot build-up and clogged EGR Valves Direct replacement. No installation instruction. No Gl...
View full detailsOriginal price $92.99 - Original price $92.99Original price$92.99$92.99 - $92.99Current price $92.99 -
For 2014-2019 3.0L Dodge Ram 1500 EcoDiesel EGR Valve & Cooler Delete Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $72.99 - Original price $72.99Original price$72.99$72.99 - $72.99Current price $72.99Material: Aluminum,Stainless steel,Silicone. Eliminates soot build-up and clogged EGR Valves. EGR removed and the temperature in the engine compa...
View full detailsOriginal price $72.99 - Original price $72.99Original price$72.99$72.99 - $72.99Current price $72.99 -
For 2006-2007 6.6L Chevrolet Silverado Classic GMC Duramax LBZ Diesel EGR Valve Cooler Delete Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $63.49 - Original price $63.49Original price$63.49$63.49 - $63.49Current price $63.49Material: Aluminum,Stainless steel,Silicone Eliminates soot build-up and clogged EGR Valves Guaranteed to last under high temperatures and pressu...
View full detailsOriginal price $63.49 - Original price $63.49Original price$63.49$63.49 - $63.49Current price $63.49 -
Seguler 2003-2007 6.0L FORD Powerstroke Diesel EGR Cooler Delete Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $56.14 - Original price $56.14Original price$56.14$56.14 - $56.14Current price $56.14Material: 304 stainless steel,Aluminum billet. Eliminate ash accumulation and EGR valve blockage. Improve the cooling effect and reduce the engi...
View full detailsOriginal price $56.14 - Original price $56.14Original price$56.14$56.14 - $56.14Current price $56.14 -
Seguler 2010-2024 6.7L Dodge Ram Cummins Diesel EGR Valve Cooler Delete Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $89.99 - Original price $89.99Original price$89.99$89.99 - $89.99Current price $89.99Material: Aluminum alloy,silicone This kit is intended for off road use. Eliminates soot build up and clogged EGR Valves. Hot exhaust gasses ar...
View full detailsOriginal price $89.99 - Original price $89.99Original price$89.99$89.99 - $89.99Current price $89.99 -
Seguler 2011-2016 6.6L GMC Chevy Duramax Diesel LML Up-Pipe & EGR Valve Cooler Delete Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $173.86 - Original price $173.86Original price$173.86$173.86 - $173.86Current price $173.86Material: 304 Stainless Steel. Reduce the amount of carbon deposited from exhaust to intake. Thanks to its fast airflow and superior engineered ex...
View full detailsOriginal price $173.86 - Original price $173.86Original price$173.86$173.86 - $173.86Current price $173.86 -
Seguler 2003-2007 6.0L Ford F250 F350 Powerstroke Diesel EGR Basic Cooler Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $79.99 - Original price $79.99Original price$79.99$79.99 - $79.99Current price $79.99CNC machine of Aluminum and Stainless Steel billets. Resist corrosion and rust for a long time and has good heat dissipation. Reduce component a...
View full detailsOriginal price $79.99 - Original price $79.99Original price$79.99$79.99 - $79.99Current price $79.99 -
For 1983-1997 Ford F150 F250 F350 Mustang Trucks EGR Delete Block Off Plate Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $22.87 - Original price $22.87Original price$22.87$22.87 - $22.87Current price $22.87Material: Aluminum alloy. Easy installation,and convenient to use. Made of CNC milled from aircraft grade Billet aluminum. Will Not Warp or Deform...
View full detailsOriginal price $22.87 - Original price $22.87Original price$22.87$22.87 - $22.87Current price $22.87 -
Seguler 2017-2019 L5P Duramax Diesel 4pcs L5P Can Bus Plugs Connector Replacement
SEGULEROriginal price $64.99 - Original price $64.99Original price$64.99$64.99 - $64.99Current price $64.99Material: ABS For use with an Aftermarket Exhaust System. A new engine calibration is required. Plugs will replace NOX and DEF modules. The L...
View full detailsOriginal price $64.99 - Original price $64.99Original price$64.99$64.99 - $64.99Current price $64.99 -
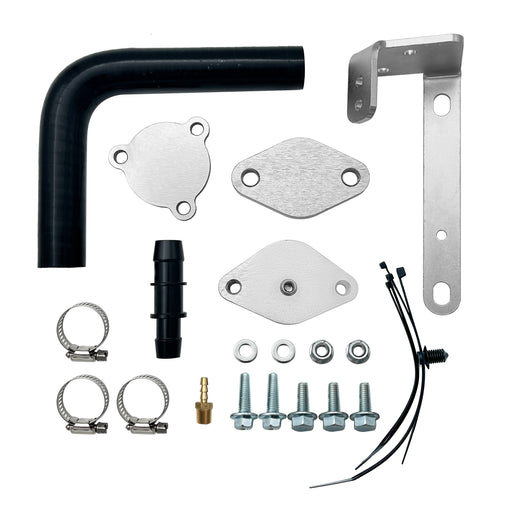
For 2011-2023 6.7L Ford F250 F350 F450 F550 Powerstroke Diesel EGR Valve Delete Cooler Delete Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $55.99 - Original price $55.99Original price$55.99$55.99 - $55.99Current price $55.99Material: Aluminum alloy,Stainless steel. Black Anodized components for better durability. 12mm Hole exhaust cover plate for Ford EGT Probes. E...
View full detailsOriginal price $55.99 - Original price $55.99Original price$55.99$55.99 - $55.99Current price $55.99 -
Seguler 2020-2023 chevy duramax L5P Diesel Can Bus Plugs Connector
SEGULEROriginal price $69.99 - Original price $69.99Original price$69.99$69.99 - $69.99Current price $69.99For use with aftermarket exhaust systems or delete pipes Used when removing the DPF/DEF systems These plugs will go in place of the NOx and DEF mo...
View full detailsOriginal price $69.99 - Original price $69.99Original price$69.99$69.99 - $69.99Current price $69.99 -
For 2017-2023 6.6L Chevy GMC Duramax L5P diesel EGR Valve Cooler Delete kit
SEGULEROriginal price $131.99 - Original price $131.99Original price$131.99$131.99 - $131.99Current price $131.99Material:Aluminum Alloy ,Stainless steel,Silica gel Improved Performance: Eliminating the EGR system leads to better exhaust flow and faster tur...
View full detailsOriginal price $131.99 - Original price $131.99Original price$131.99$131.99 - $131.99Current price $131.99 -
Seguler 3" Ecodiesel DPF Delete Pipe & EGR Delete kit for 2014-2018 3.0L Ram
SEGULEROriginal price $342.00 - Original price $342.00Original price$342.00$342.00 - $342.00Current price $342.00Material: High quality stainless steel Inlet Diameter: 3.0" Eliminates soot build-up and clogged EGR Valves Specialized designs to ensure a perfec...
View full detailsOriginal price $342.00 - Original price $342.00Original price$342.00$342.00 - $342.00Current price $342.00 -
For 2007-2010 Cummins ISX CM871 EGR Plug Kit Stage 2 Plates and Plugs Aluminum
SEGULEROriginal price $67.99 - Original price $67.99Original price$67.99$67.99 - $67.99Current price $67.99Material:304 Stainless Steel & Billet Aluminum. High-temperature graphite gaskets are adopted to prevent leakage. Used to delete the EGR val...
View full detailsOriginal price $67.99 - Original price $67.99Original price$67.99$67.99 - $67.99Current price $67.99 -
For 11-23 Ford 6.7L Powerstroke CCV/PCV Reroute/Delete Engine Ventilation Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $72.00 - Original price $72.00Original price$72.00$72.00 - $72.00Current price $72.00Material:Aluminum alloy rubber. Black Anodized components for better durability. This Crankcase Ventilation System provides a SOLID solution to ...
View full detailsOriginal price $72.00 - Original price $72.00Original price$72.00$72.00 - $72.00Current price $72.00 -
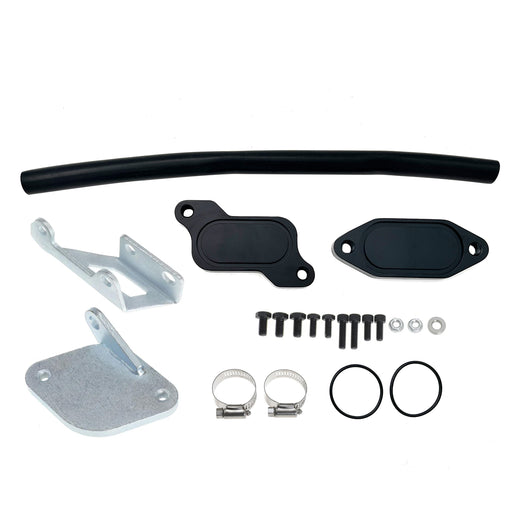
For 2013-2023 6.7L Dodge Ram Cummins Cab & Chassis EGR Delete Kit Diesel
SEGULEROriginal price $62.99 - Original price $62.99Original price$62.99$62.99 - $62.99Current price $62.99Material: Aluminum alloy. Eliminates soot build up and clogged EGR Valves. Hot exhaust gasses are not being re-routed back into the motor. Coo...
View full detailsOriginal price $62.99 - Original price $62.99Original price$62.99$62.99 - $62.99Current price $62.99 -
For 2007-2010 6.6L Chevy GMC LMM Duramax EGR Valve Cooler Delete Kit Fit
SEGULEROriginal price $61.99 - Original price $61.99Original price$61.99$61.99 - $61.99Current price $61.99Material: Aluminum alloy,Stainless steel. Improves engine life by eliminating soot build-up and reducing fuel consumption. EGR valve cooler delet...
View full detailsOriginal price $61.99 - Original price $61.99Original price$61.99$61.99 - $61.99Current price $61.99 -
For 2013-2018 6.7L Dodge RAM 2500 3500 Cummins Diesel EGR Delete Cooler Throttle Valve Delete Kit
SEGULEROriginal price $112.00 - Original price $112.00Original price$112.00$112.00 - $112.00Current price $112.00Material: Aluminum alloy,silicone Aluminum material can resist corrosion and rust for a long time and has good heat dissipation. EGR delete stan...
View full detailsOriginal price $112.00 - Original price $112.00Original price$112.00$112.00 - $112.00Current price $112.00

























Leave a comment